-
Product Name
Mouse CD83 (Fc Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. CD83 is considered as a marker of mature dendritic cells as well as an adhesion receptor that binds to resting monocytes and a subset of activated CD8+ T cells. In certain conditions, CD83 tended to dimerize or even multimerize through its aberrant intermolecular disulfide bonds. The injection of CD83-Ig can significantly enhaunce the rate of tumor growth and inhibit the T cell growth.
-
Protein name
CD83 antigen
-
Protein short names
CD83; BL11; MGC130312; MGC130313; HB15
-
Uniprot ID
O88324
-
Gene Name
Cd83
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse CD83 (O88324) (Met 1-Arg 133) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Mouse
-
Molecular weight
The secreted recombinant mouse CD83/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 353 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 39.2 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rm CD83/Fc monomer is approximately 50-55 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
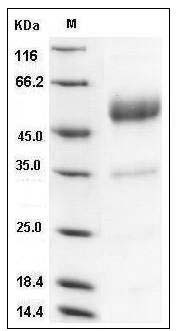
Mouse CD83 / HB15 Protein (Fc Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
