-
Product Name
H1N1 HA (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Binds to sialic acid-containing receptors on the cell surface, bringing about the attachment of the virus particle to the cell. This attachment induces virion internalization of about two third of the virus particles through clathrin-dependent endocytosis and about one third through a clathrin- and caveolin-independent pathway. Plays a major role in the determination of host range restriction and virulence. Class I viral fusion protein. Responsible for penetration of the virus into the cell cytoplasm by mediating the fusion of the membrane of the endocytosed virus particle with the endosomal membrane. Low pH in endosomes induces an irreversible conformational change in HA2, releasing the fusion hydrophobic peptide. Several trimers are required to form a competent fusion pore.
-
Protein name
Hemagglutinin
-
Protein short names
HA; CTLO; SPH; C-H-RAS; C-HA-RAS1; SPNA1; HAMSV; H-RASIDX; C-BAS/HAS; SPNA-1; RASH1; AF093576; AI451697; IHJ; NMF4; P21RAS; HRAS1
-
Uniprot ID
Q9WFX4
-
Gene Name
HA
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the Influenza A virus (A/New York/1/1918(H1N1)) hemagglutinin (AAD17219.1) (Met1-Arg344), termed as HA1, was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
H1N1
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant HA1 subunit of the Influenza A virus (A/New York/1/1918(H1N1)) consists 338 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 37.5 kDa.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
Validations
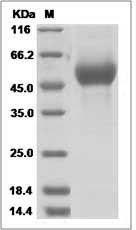
Influenza A H1N1 (A/New York/1/1918) Hemagglutinin Protein (HA1 Subunit) (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
