-
Product Name
Cynomolgus Epcr/PROCR (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
Endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), also known as activated protein C receptor (APC receptor) or PROCR, is a receptor for Protein C. Protein C plays an important role in many metabolism processes in humans and other animals after activated by binding to Endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR). Because of the EPCR is found primarily on endothelial cells (cells on the inside of blood vessels), activated protein C is found maily near endothelial cells. Protein C is pleiotropic, with two main functions: anticoagulation and cytoprotection. Which function will be performed depend on whether or not protein C remains bind to EPCR after activated. The anticoagulation occurs when it does not. In this case, protein C functions as an anticoagulant by irreversibly proteolytically inactivating Factor Va and Factor VIIIa, turning them into Factor Vi and Factor VIIIi respectively. When still bound to EPCR, activated protein C performs its cytoprotective effects, acting on the effector substrate PAR-1, protease-activated receptor-1. To a degree, APC's anticoagulant properties are independent of its cytoprotective ones, in that expression of one pathway is not affected by the existence of the other.
-
Protein short names
CD201; BA42O4.2; RP23-388H13.2; MGC23024; EPCR; CCCA; AI325044; CCD41
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus PROCR (Met1-Thr209) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Cynomolgus
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant cynomolgus PROCR comprises 203 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 23.3 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of it is approximately 35-40 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Validations
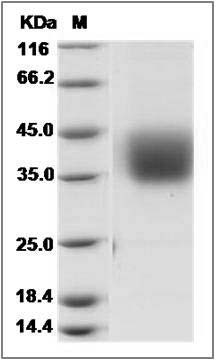
Cynomolgus Epcr / PROCR Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
