-
Product Name
Cynomolgus ACVR2B (His Tag) recombinant protein
- Documents
-
Description
ACVR2A and ACVR2B are two activin type II receptors. ACVR2B is integral to the activin and myostatin signaling pathway. Ligands such as activin and myostatin bind to ACVR2A and ACVR2B. Myostatin, a negative regulator of skeletal muscle growth, is regarded as a potential therapeutic target and binds to ACVR2B effectively, and to a lesser extent, to ACVR2A. The structure of human ACVR2B kinase domain in complex with adenine establishes the conserved bilobal architecture consistent with all other catalytic kinase domains. Haplotype structure at the ACVR2B and follistatin loci may contribute to interindividual variation in skeletal muscle mass and strength. Defects in ACVR2B are a cause of left-right axis malformations.
-
Protein short names
MGC118477; ACVR2B; ACTRIIB; HTX4; MGC116908; ACTR-IIB
-
Source/Expression Host
Human Cells
-
Expression Plasmid/cDNA
A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus ACVR2B (Ser28-Thr143) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
-
Protein Species
Cynomolgus
-
Molecular weight
The recombinant cynomolgus ACVR2B comprises 127 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 14.8 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of it is approximately 33-36 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
-
Purity
> 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
-
Activity
Measured by its ability to neutralize Activin-mediated inhibition on MPC11 cell proliferation.
The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-1 µg/mL in the presence of 10 ng/mL recombinant Activin A. -
Validations
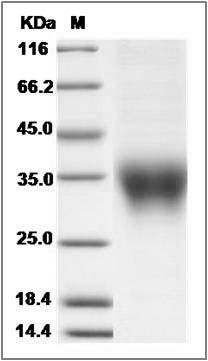
Cynomolgus ACVR2B / ACTRIIB Protein (His Tag) SDS-PAGE
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
