-
Product Name
Anti-TH / Tyrosine Hydroxylase antibody
- Documents
-
Description
Rabbit polyclonal to TH / Tyrosine Hydroxylase
-
Tested applications
WB, IF, IP, ICC/IF
-
Species reactivity
Human Tyrosine Hydroxylase/TH
-
Alternative names
DYT14 antibody; OTTMUSP00000020341 antibody; Th antibody; TYH antibody; TYH antibody; DYT14 antibody; DYT5b antibody; Tyrosine Hydroxylase antibody; DYT5b antibody; TH antibody; tyrosine 3-hydroxylase antibody; tyrosine 3-monooxygenase antibody; Tyrosine Hydroxylase antibody
-
Isotype
Rabbit IgG
-
Preparation
Produced in rabbits immunized with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminus of the Human Tyrosine Hydroxylase/TH, and purified by antigen affinity chromatography.
-
Clonality
Polyclonal
-
Formulation
0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS
-
Storage instructions
This antibody can be stored at 2℃-8℃ for one month without detectable loss of activity. Antibody products are stable for twelve months from date of receipt when stored at -20℃ to -80℃. Preservative-Free.
Sodium azide is recommended to avoid contamination (final concentration 0.05%-0.1%). It is toxic to cells and should be disposed of properly. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. -
Applications
WB: 10-20 μg/ml
ICC/IF: 0.5-1.5 μg/mL
IP: 1-4 uL/mg of lysate
-
Validations

Tyrosine Hydroxylase / TH Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified, Western blot
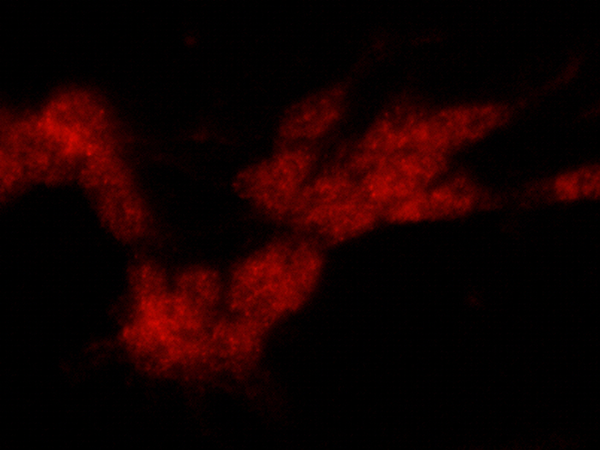
Tyrosine Hydroxylase / TH Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified, Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence staining of TH in SHSY5Y cells. Cells were fixed with 4% PFA, permeabilzed with 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS,blocked with 10% serum, and incubated with rabbit anti-human TH polyclonal antibody (1 µg/ml) at 4℃ overnight. Then cells were stained with the Alexa Fluor®594-conjugated Goat Anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (red)Positive staining was localized to cytoplasm and nucleus.
-
Background
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is a rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine synthesis. Tyrosine hydroxylase activity is modulated by protein-protein interactions with enzymes in the same pathway or the tetrahydrobiopterin pathway, structural proteins considered to be chaperones that mediate the neuron's oxidative state. It is phosphorylated at serine (Ser) residues Ser8, Ser19, Ser31 and Ser40 in vitro. The phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase at Ser19 or Ser8 has no direct effect on tyrosine hydroxylase activity. As tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) catalyses the formation of L-DOPA, the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of DA, the Parkinson's disease (PD) can be considered as a TH-deficiency syndrome of the striatum. A direct pathogenetic role of TH has also been suggested, as the enzyme is a source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in vitro and a target for radical-mediated oxidative injury. Recently, it has been demonstrated that L-DOPA is effectively oxidized by mammalian Tyrosine hydroxylase in vitro, possibly contributing to the cytotoxic effects of DOPA.
-
References
- Daubner SC, et al. (2011) Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 508(1): 1-12.
- Dunkley PR, et al. (2004) Tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation: regulation and consequences. J Neurochem. 91(5): 1025-43.
- Haavik J, et al. (1998) Tyrosine hydroxylase and Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 16(3): 285-309.
Related Products / Services
Please note: All products are "FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND ARE NOT INTENDED FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE"
